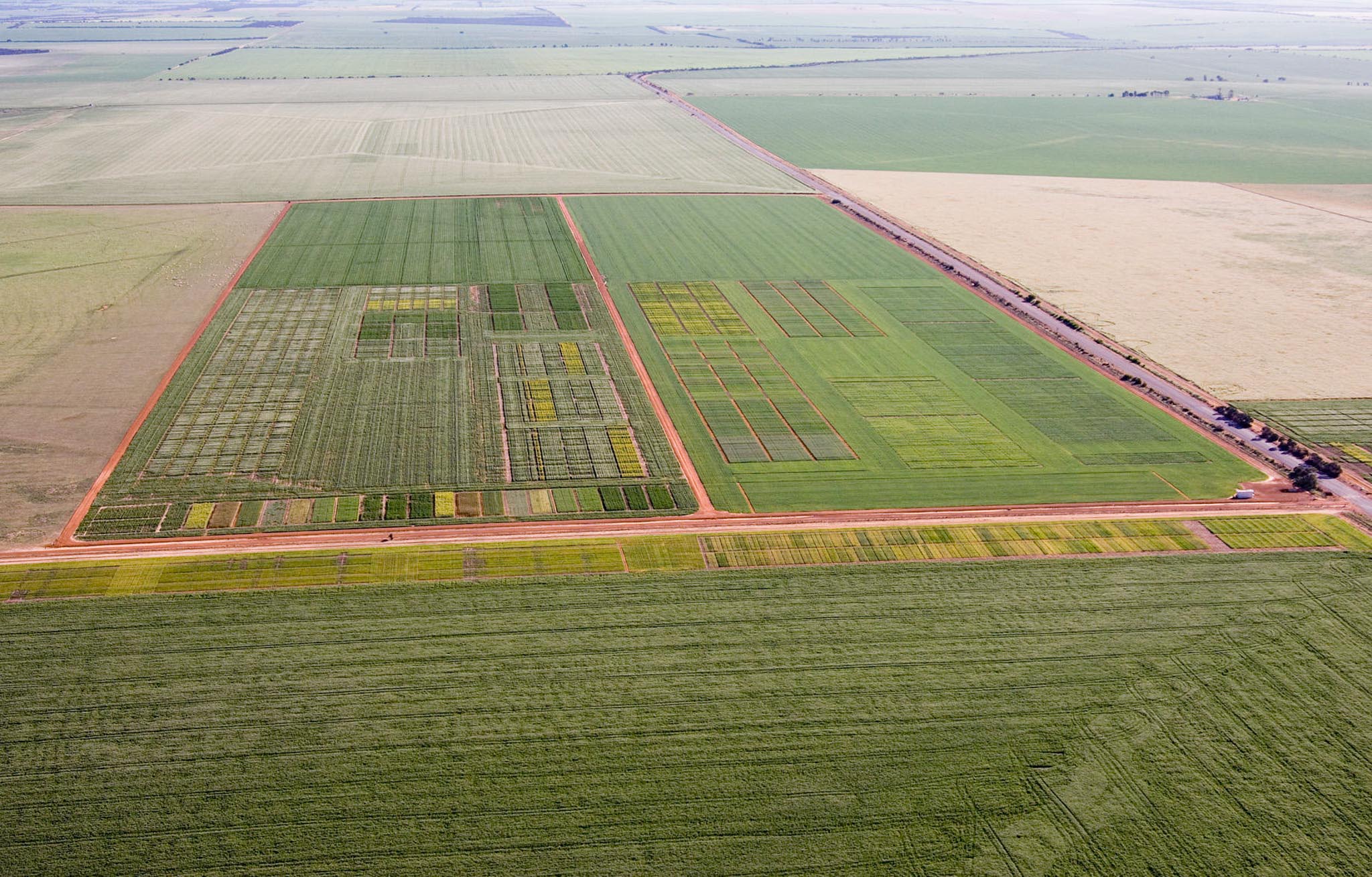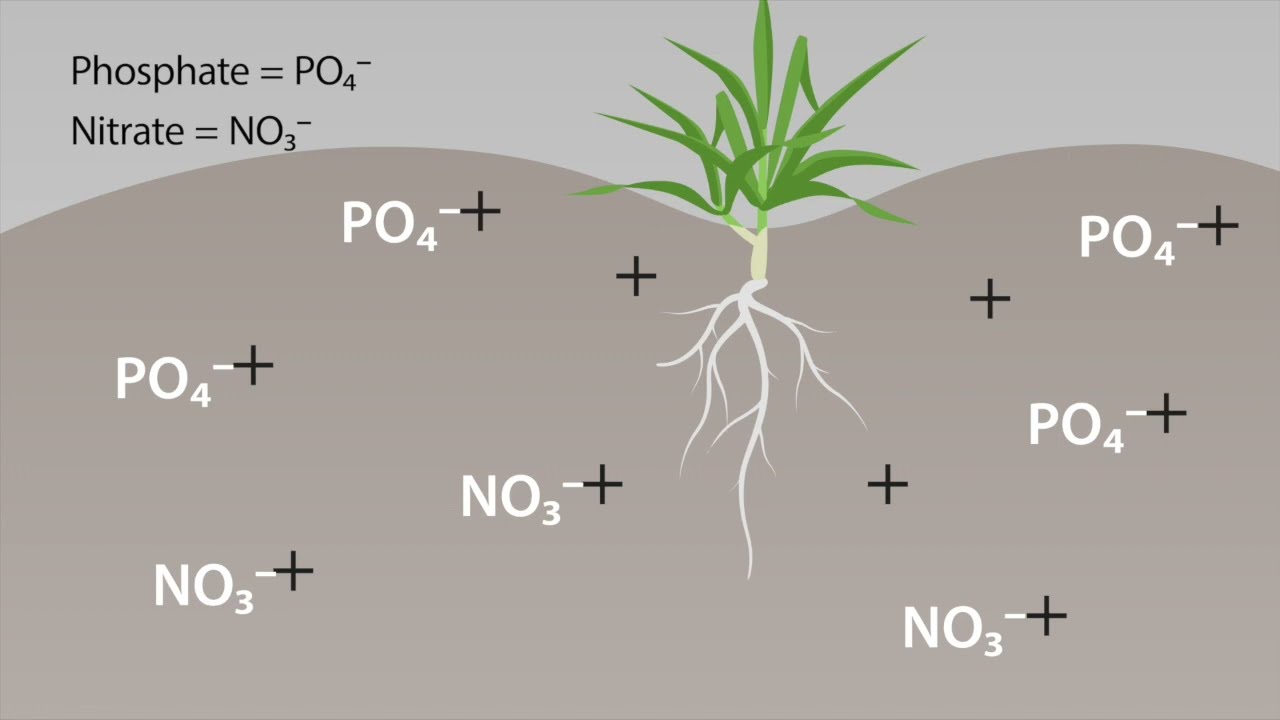
Unlike most soil types, gravel soil possesses anion exchange capacity in addition to cation exchange capacity, adding complexity to how nutrient interactions are controlled.

A combination of crop choice, water harvesting, gypsum application, maximising soil cover and no livestock, and then maintaining the improved surface soil structure with controlled traffic, mean that the Nixon’s sodic and alkaline soil is productive.

Soil pit demonstration of sandy duplex soil presented by Matthias Leopold at Pingelly, Western Australia.
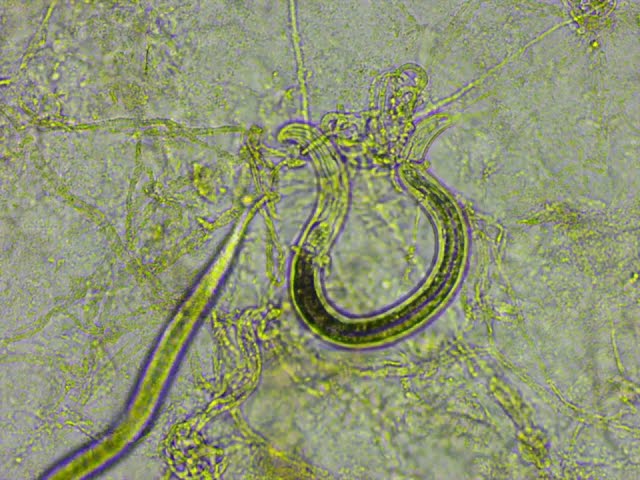
A diverse range of soil organims minimise the impact of pest nematodes via mechanisms such as predation, parasitisation, production of toxins or enzymes, competition for space and resources, entrapment, and inducing plant resistance.

Plants experience osmotic stress when they are exposed to salinity in soil.

Want to know more about soil sodicity and salinity? Watch this short video from the Understanding Your Soils Series from Soil Science Australia.
soilquality.org.au

Want to know more about Soil Horizons? Watch this short video from the Understanding Your Soils Series from Soil Science Australia.
soilquality.org.au
This NSW DPI Soils Network of Knowledge (SNoK) webinar will delve into the history of the Phosphorus Buffering Index (PBI), what soil characteristics drive PBI values and how we utilise and interpret PBI in both agronomic and environmental settings.
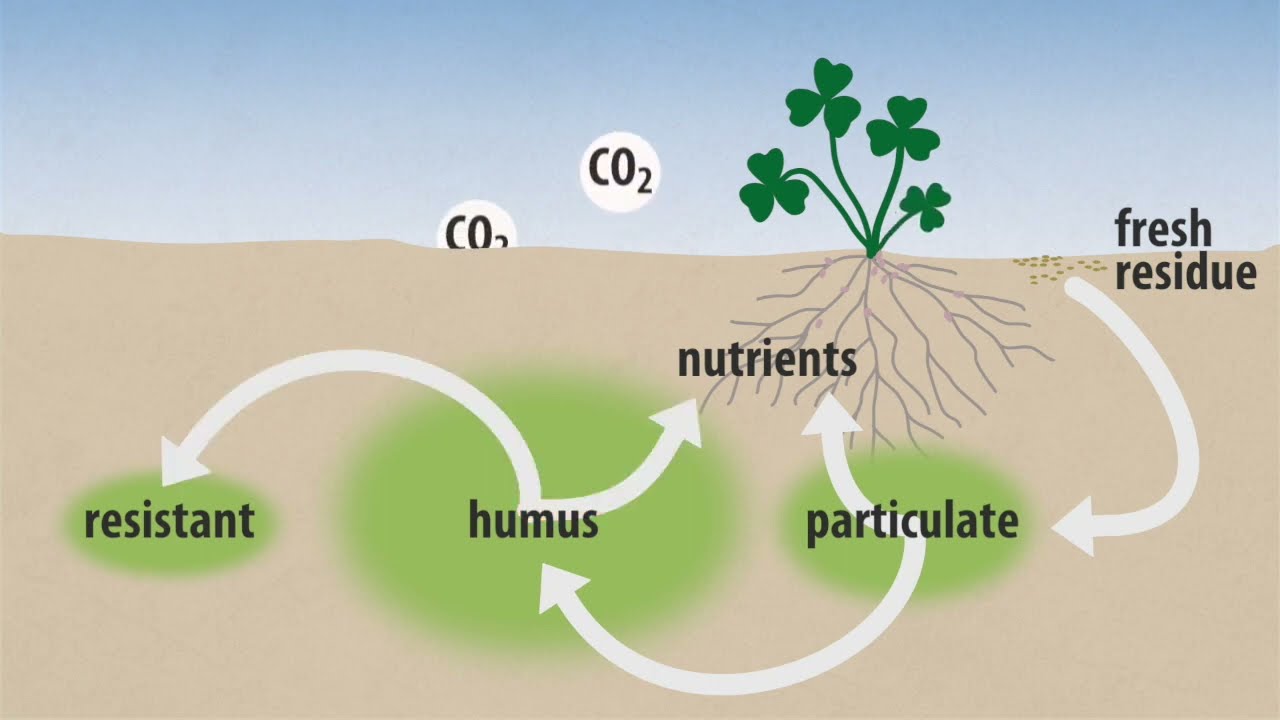
Soil organic matter turnover is continuous, occurring at at annual rate of 2-4%.



