Understand soil structural features and their impacts
The Soil physical attributes section contains information on topics including soil processes, physical soil properties and the soil structural matrix. Pages within present an overview of the current state of knowledge of soil physical attributes, explain the principles and properties of different features, highlight insights from research, and Resources are suggested throughout.
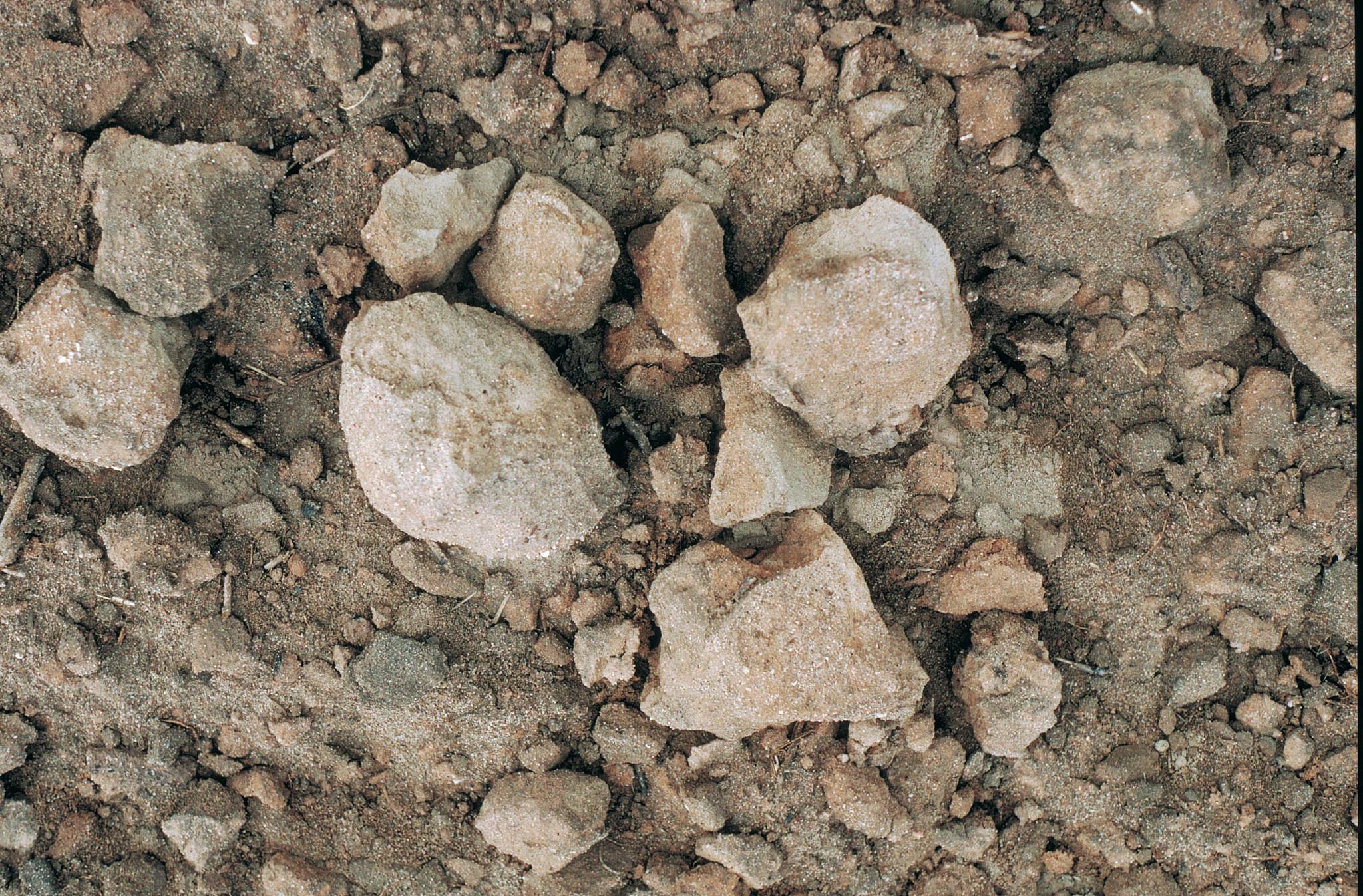
Gravel soil
Soil containing abundant ironstone gravel has poorer water holding capacity than soil of the same texture without gravel. Gravel varies in porosity which influences the extent of water and nutrient exchange within the soil profile.
Soil stability
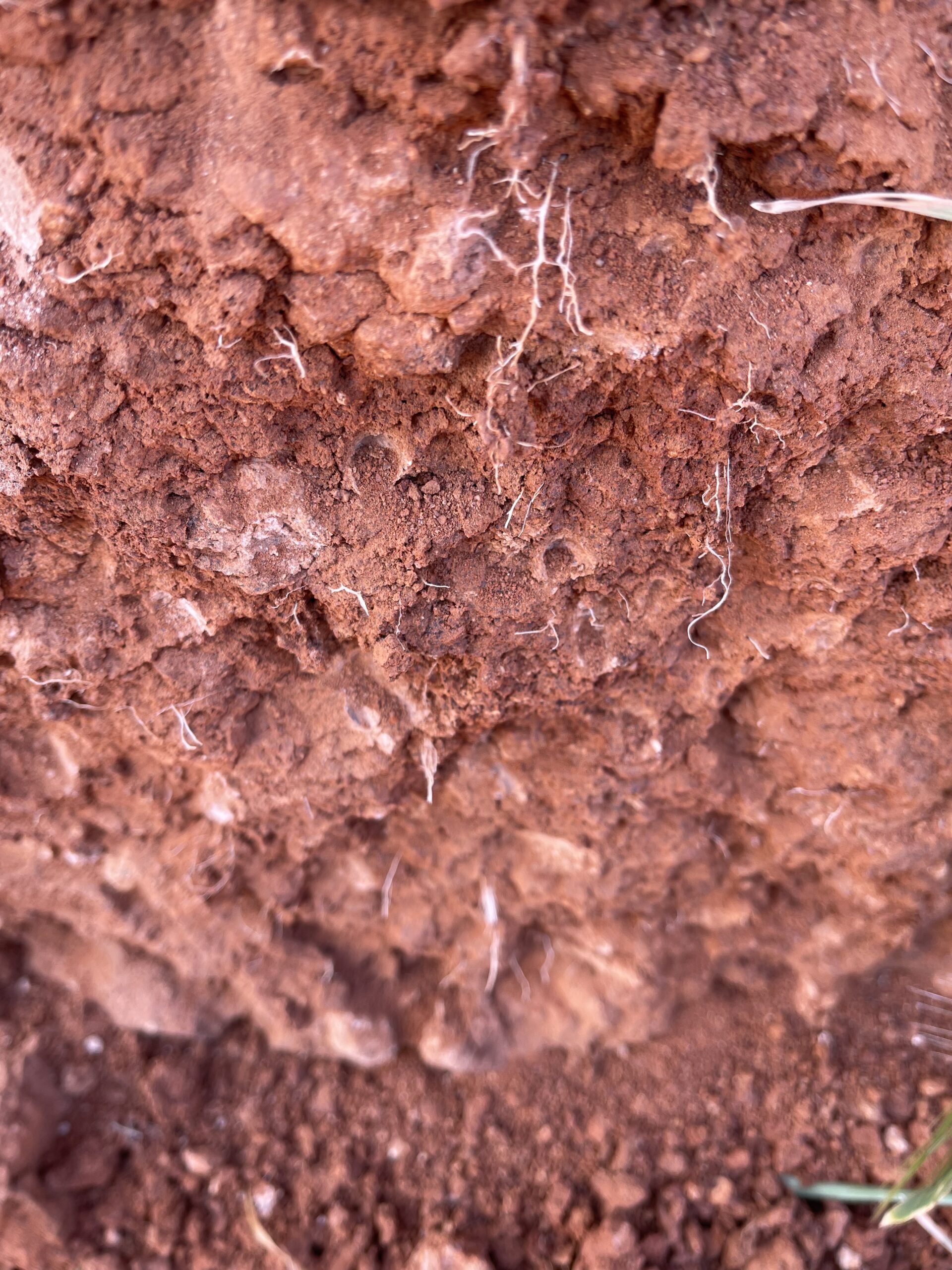
Soil consists of mineral particles (sand, silt and clay) and organic matter that will generally bind together to form aggregates; air and water that will be held in the soil pores, and soil organisms. Soil stability refers to the ability of a soil to maintain structural integrity on wetting.
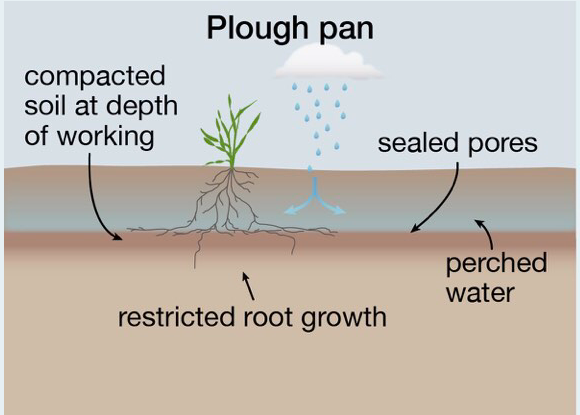
Soil compaction
Soil compaction occurs when soil particles are packed closer together. Compacted soil is stronger, denser and less porous. Less water and gas exchange occurs in a compacted soil, slowing root growth and inhibiting both water and nutrient uptake.
Soil erosion
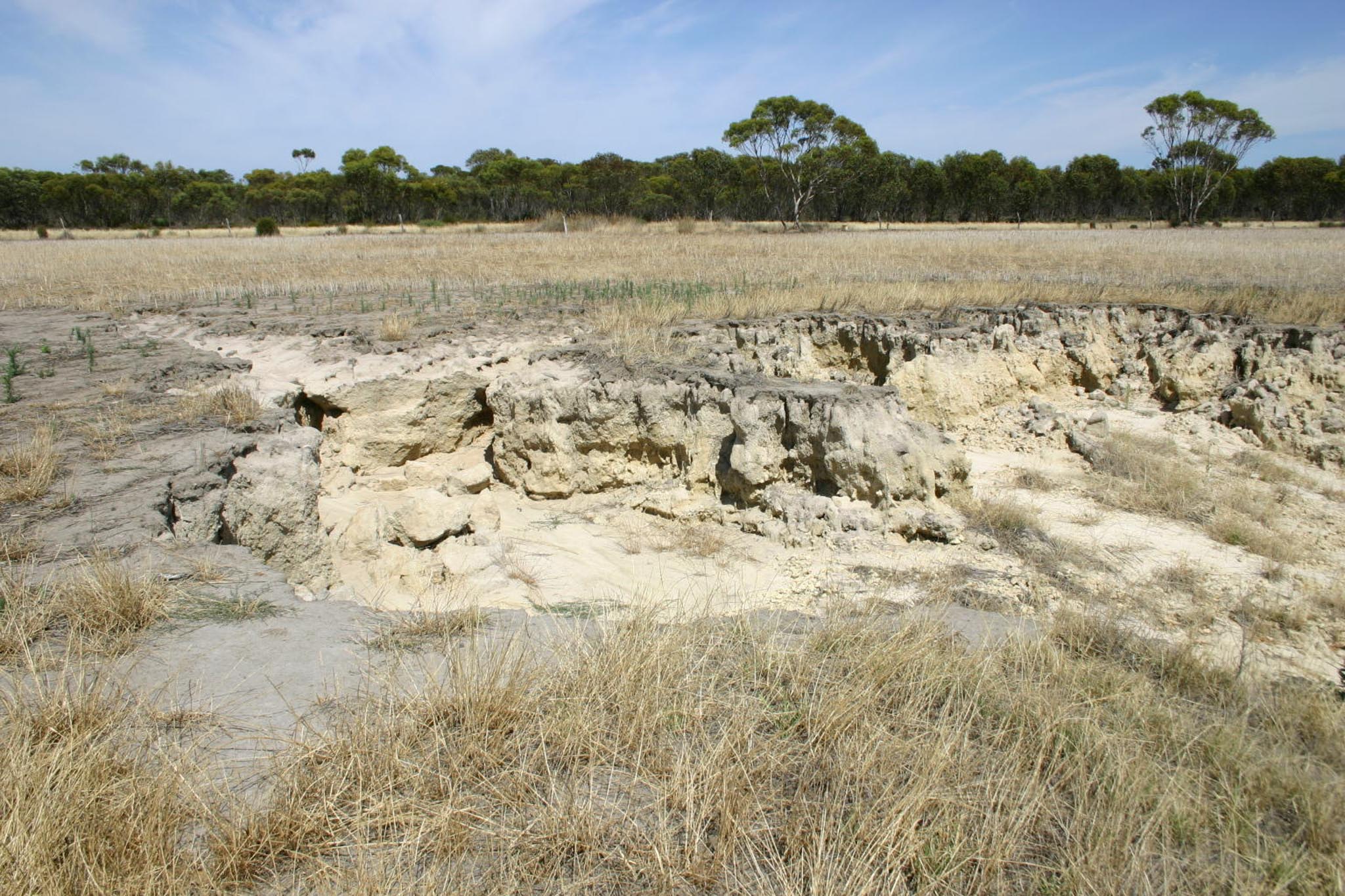
Wind and water erosion result in the rapid loss of soil, nutrients and organic matter essential for plant growth. Deposition of this soil into sensitive environments such as waterways can impact ecosystem health.
Soil water
Soil is made up of solid particles, with gases, organic matter and water occupying the spaces in between – rather like a sponge. The chemical and physical nature of the soil influences water movement into and through the soil matrix.
Soil water repellence
Soil that exhibits beading of water after rainfall or irrigation is referred to as water repellent. Repellent soil resists water entry and infiltration, so water flows unevenly via preferred pathways, leaving other parts of the soil dry.
Waterlogging
Waterlogging is a highly variable phenomenon, associated with rapid seasonal changes in water-table levels. As a result of waterlogging, processes in the soil profile affect plant growth and crop production.
Browse soil physical attribute resources
Explore our collection of journal articles, ebooks, fact sheets, graphics, website links and more.
Soil water repellence: the essentials
This video provides an outline of the causes, impacts and management of soil water repellence.
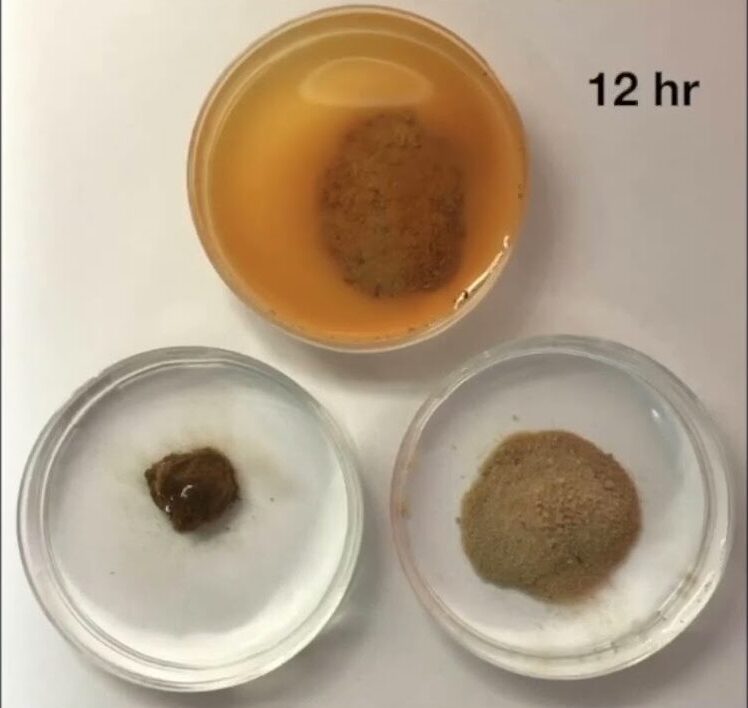
Soil stability demonstration
This short demonstration shows differing degrees of breakdown of soil aggregates when immersed in deionised water for 24 hours....
Claying to ameliorate soil water repellence
Claying can be one of the most effective ways to overcome soil water repellence.