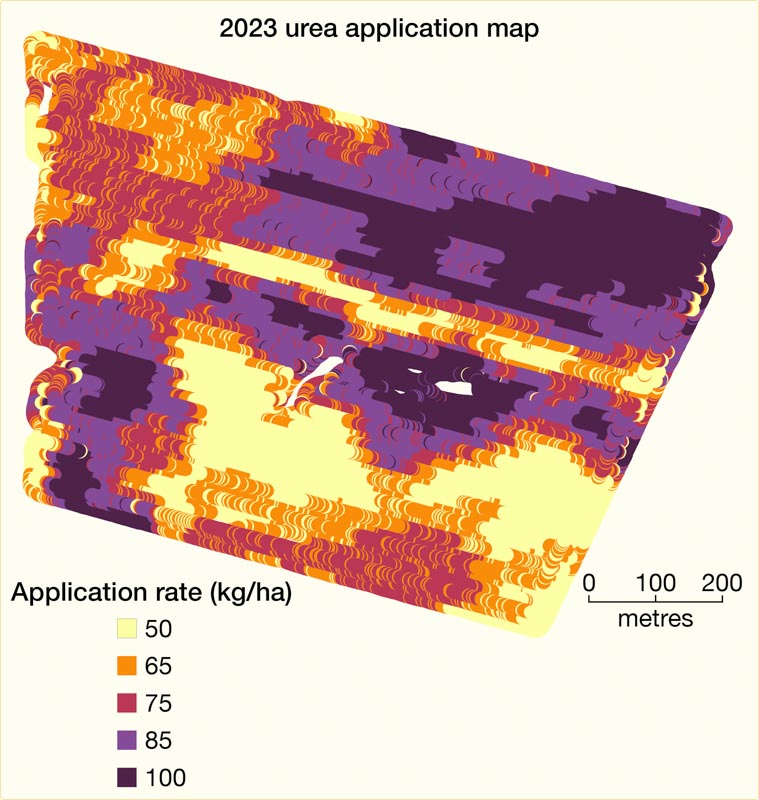
Learn how soil testing and monitoring can unlock potential
The Soil analysis and testing section provides information on how soil attributes and properties are measured and tested, as well as guidance on how to analyse and interpret soil test results and set up soil sampling and monitoring. Resources are suggested throughout.
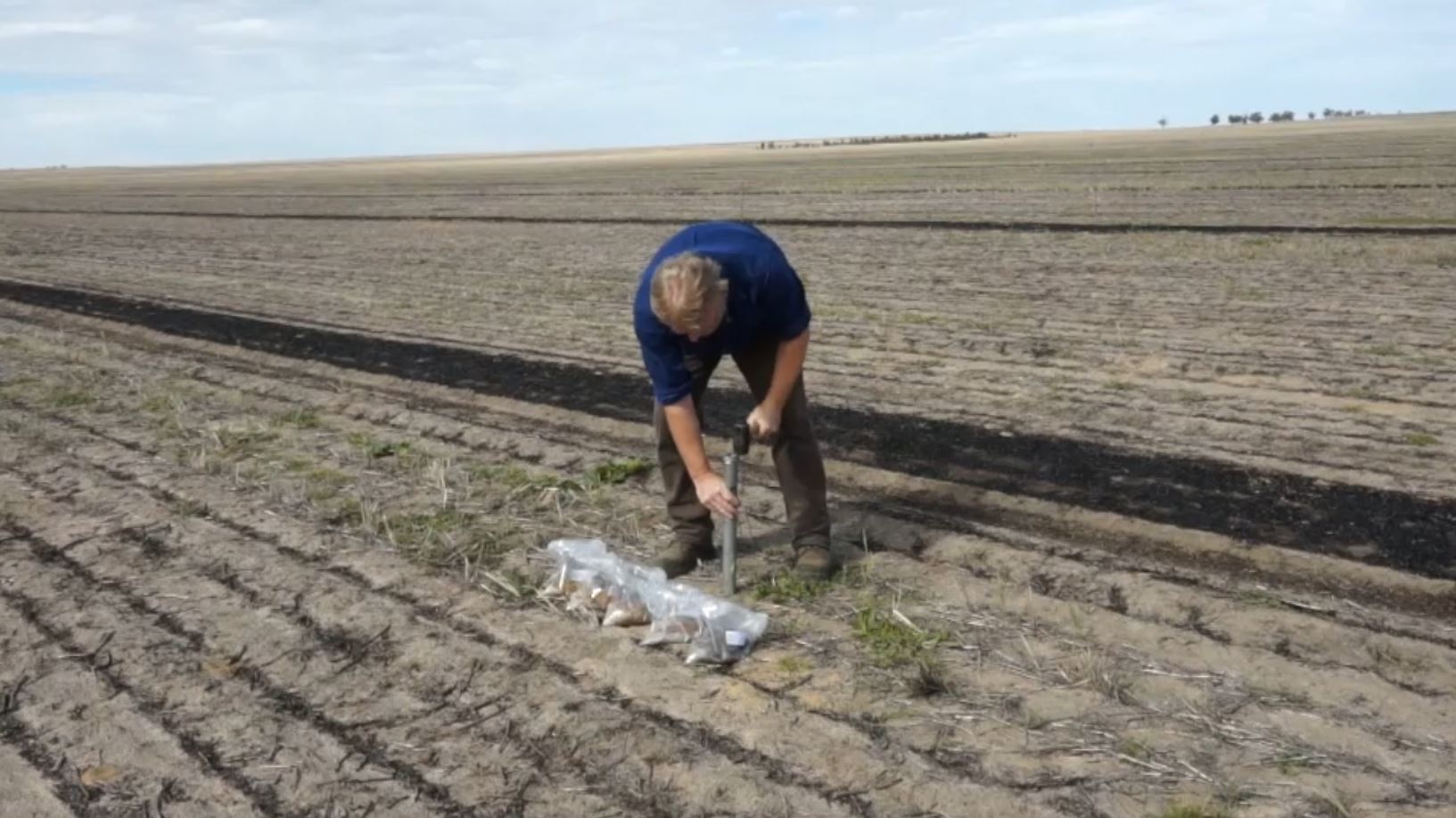
Soil sampling
Soil testing can be a relatively simple, cost effective management strategy to help optimise profitability and correctly identify important soil problems.
Soil groups and soil classification
Australia’s agricultural landscapes support a great range of soils. Most are ancient, strongly weathered and infertile by world standards. Classifying soils involves grouping soils with similar properties into one class and separating them from soils that have dissimilar properties.
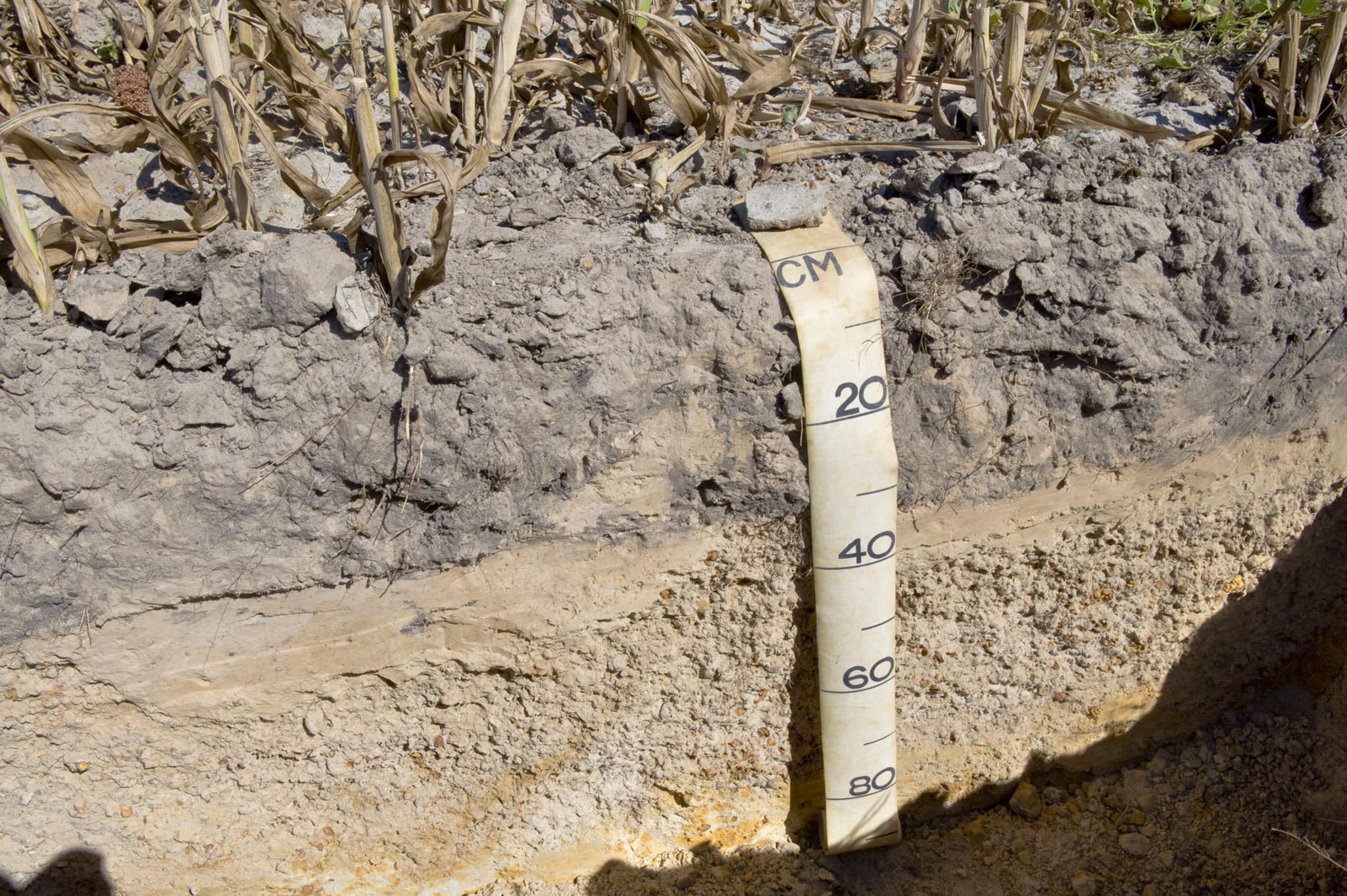
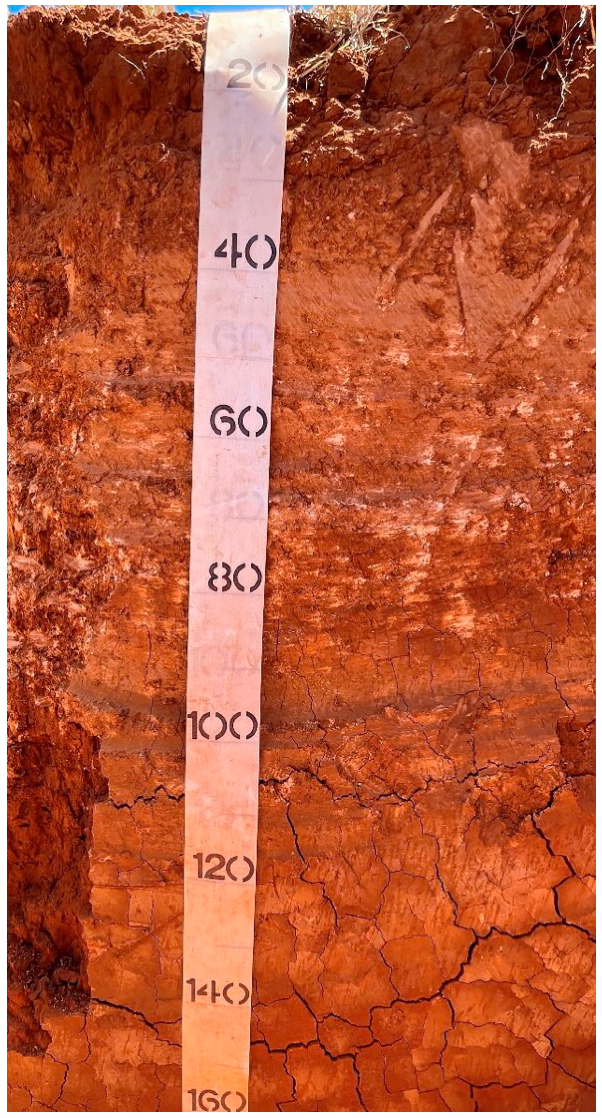
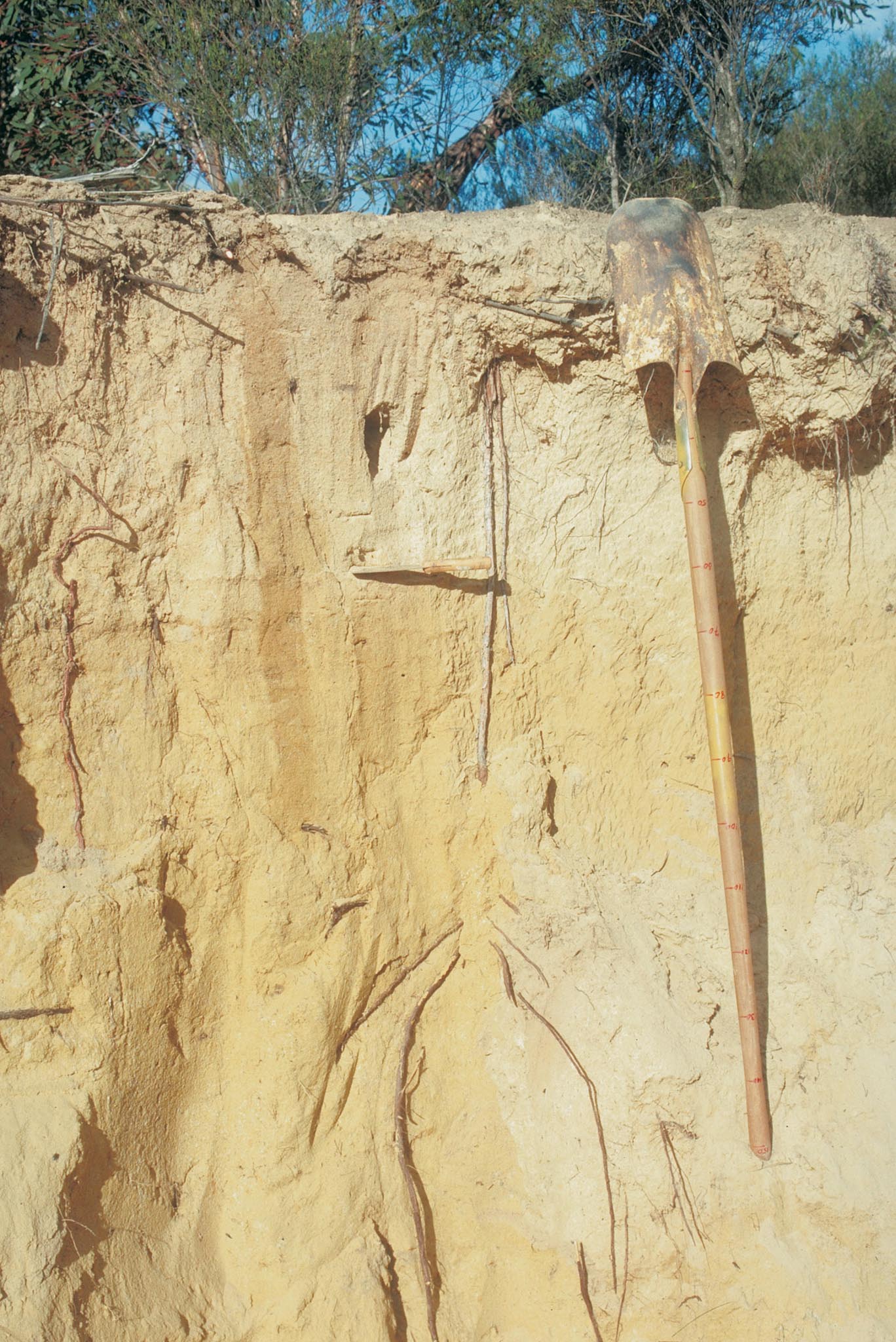
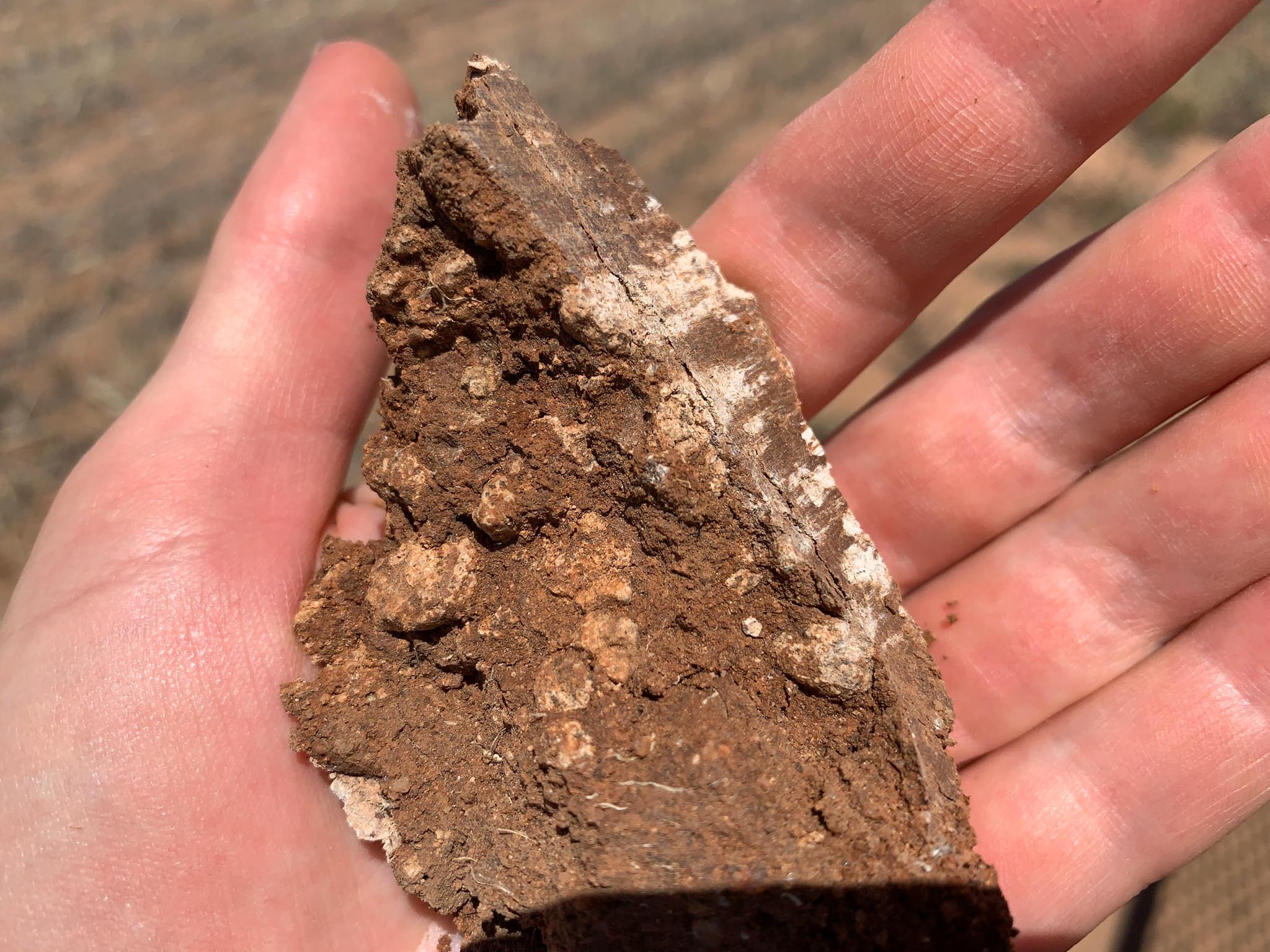
Testing soil colour
Soil colour is an important indicator of internal drainage characteristics and may help distinguish different soil layers
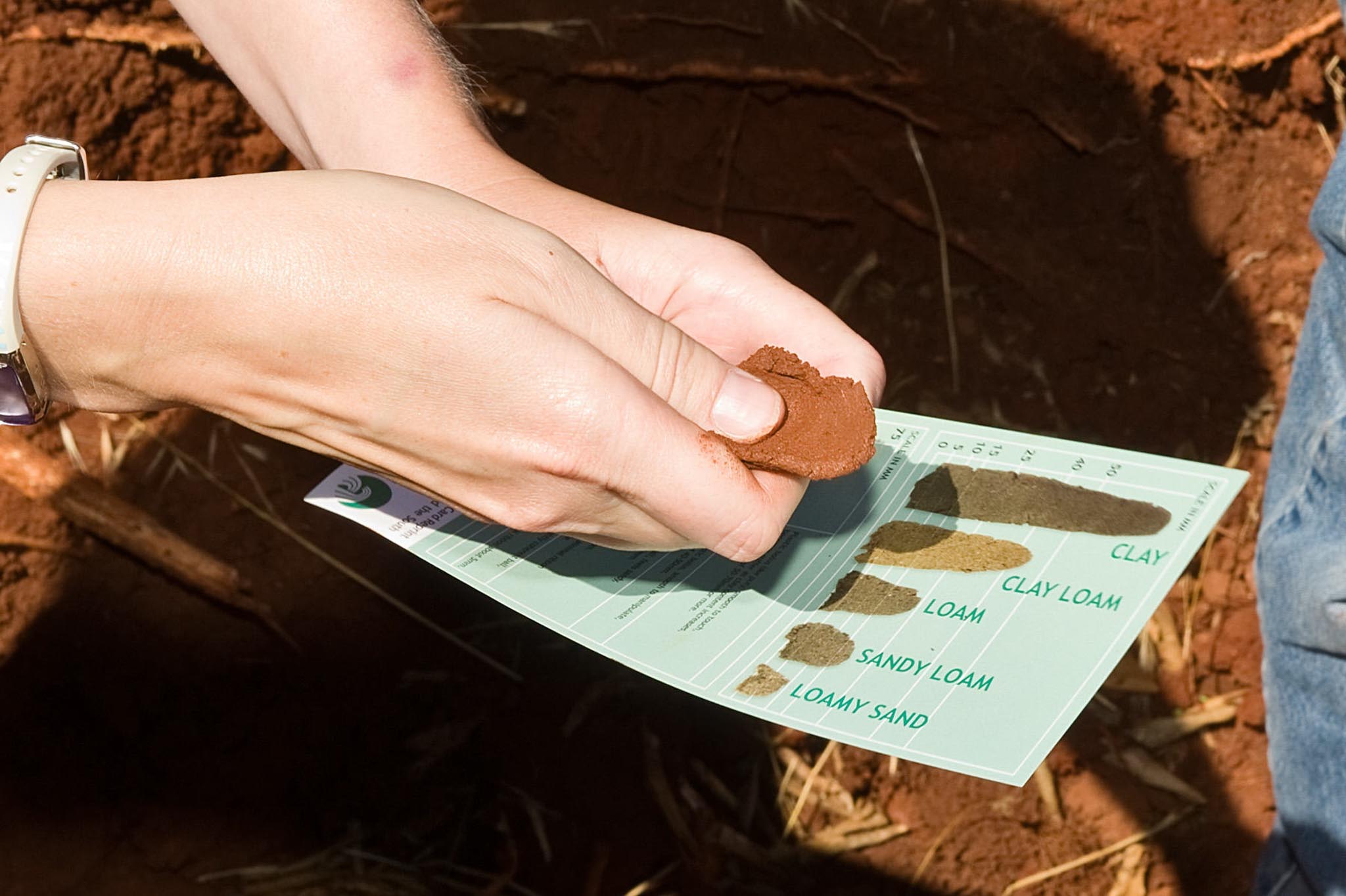
Testing soil texture
The proportions of sand, silt and clay particles in the soil determine soil texture. Soil texture affects the physical properties of soil, and in particular the storage of air and water, soil organic matter content, transmission of water and nutrients, ease of root growth, workability and resistance to erosion.
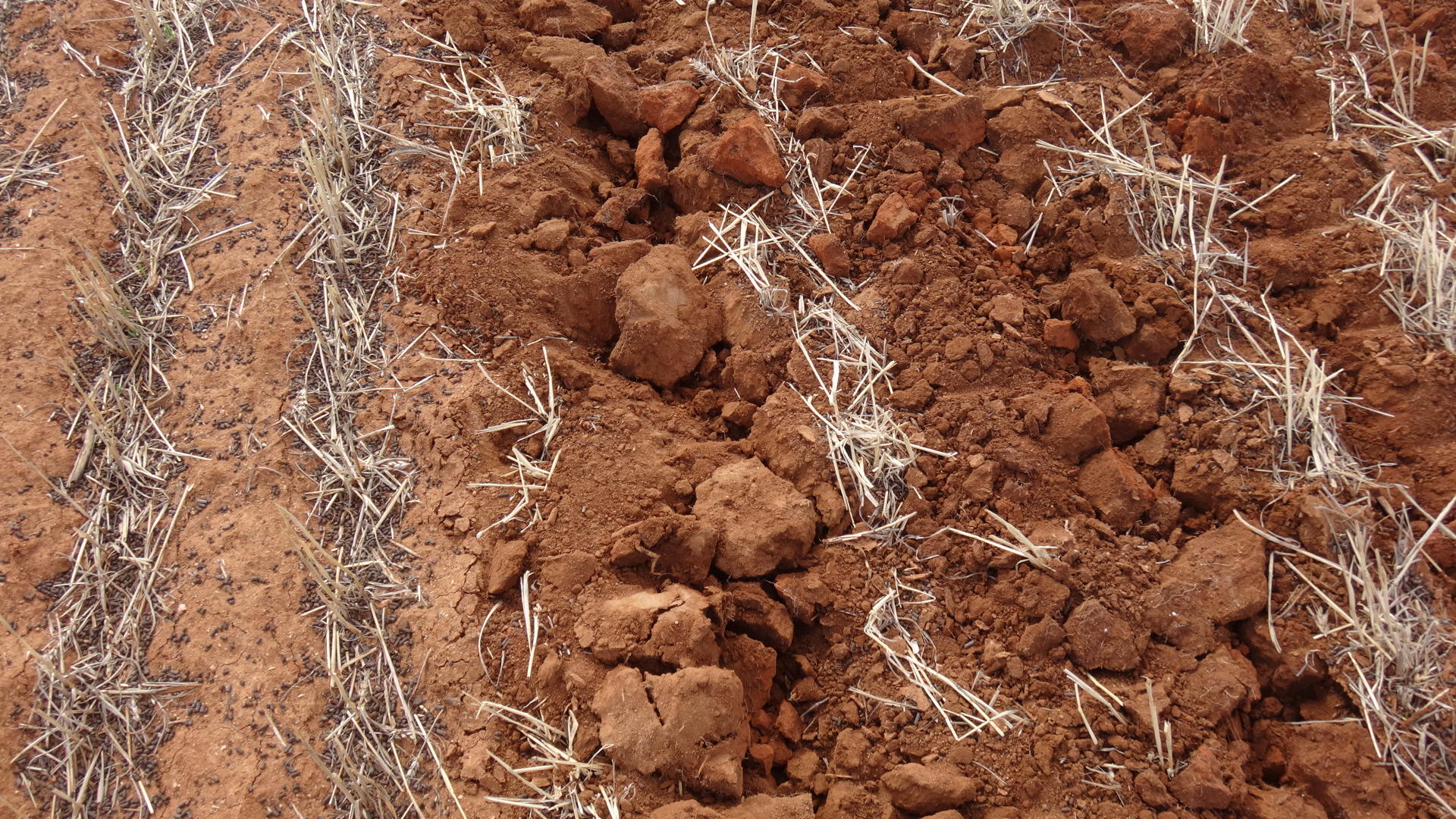
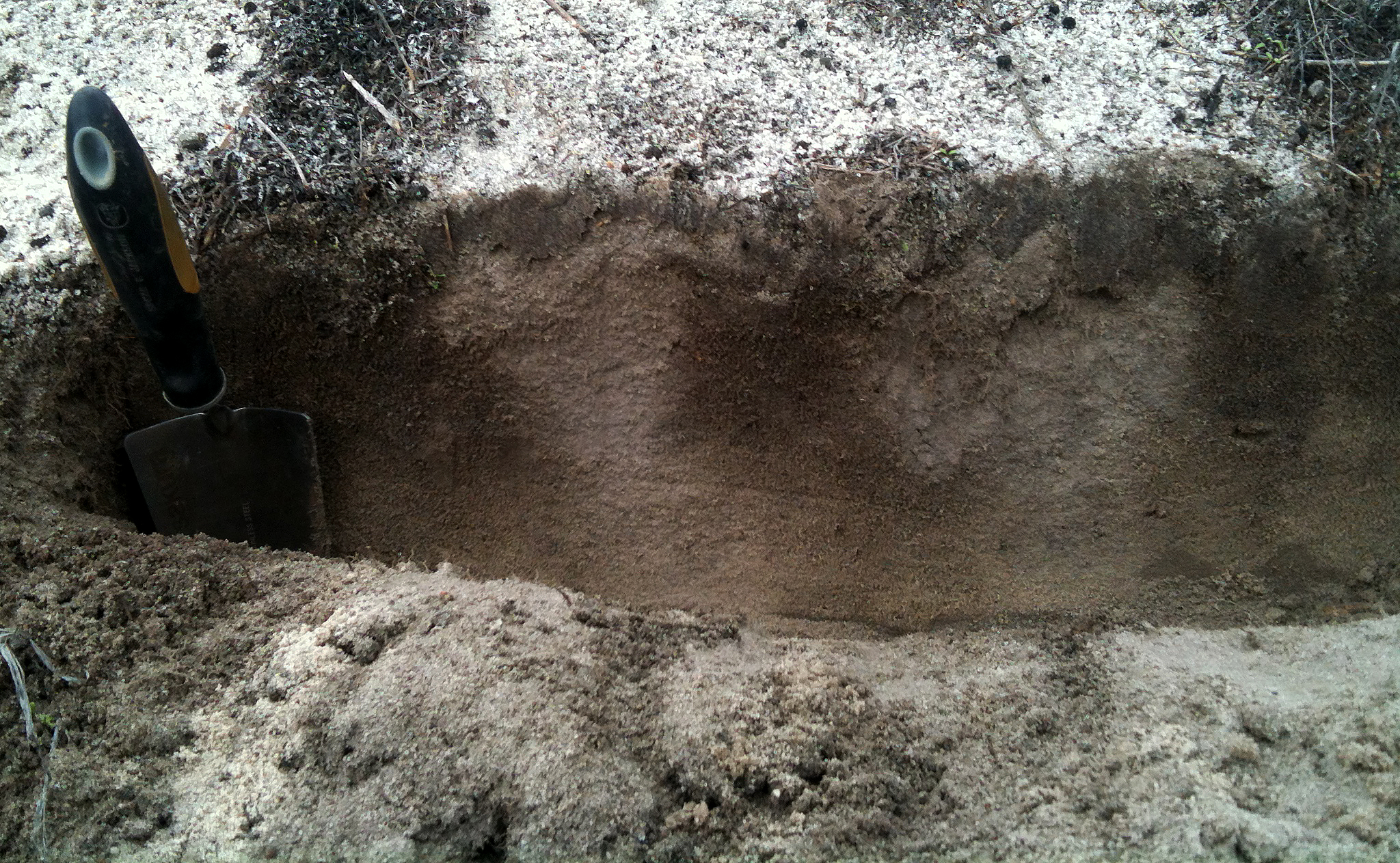
Testing soil structure
Soil structure influences movement of water, air and roots. Soil structure can be described as different geometric shapes.
Testing soil nutrients
Results from soil chemistry testing can be used to manage soil more effectively. In most cases, conditions that restrict plant growth can be easily detected by soil testing.
Identifying soil constraints
Often, multiple constraints co-exist in the topsoil and subsoil. Simple tools and observations can identify how a soil may be limiting plant production to determine the appropriate management options.
Measuring soil organic carbon
Soil is rich with living organisms, and these are closely associated with soil organic matter. Measuring these features and understanding what they mean can have consequences for soil management.
Understanding trial results and on-farm experimentation
The replication of treatments a number of times across a trial gives some level of confidence that the results measured are indeed a result of the treatments applied and not the result of natural random variation.
Browse soil analysis and testing resources
Explore our collection of journal articles, ebooks, fact sheets, graphics, website links and more.
Do-it-yourself soil sampling with exhaust tube
Do-it-yourself soil sampling requires a dedication to the task with inputs of time for sampling, arranging testing, sourcing recommendations...
Soil phosphorus testing: Colwell P and DGT-P
Different soil testing methods measure different pools of phosphorus in the soil.
Testing for dispersion and slaking
Simple guide to testing for dispersion