Date
2023/10/27
Duration
4 min read
ebook
Soil Quality: 10 Plant Nutrition
Organisations
SoilsWest
Department of Primary Industries and Regional Development
Murdoch University
Grains Research and Development Corporation
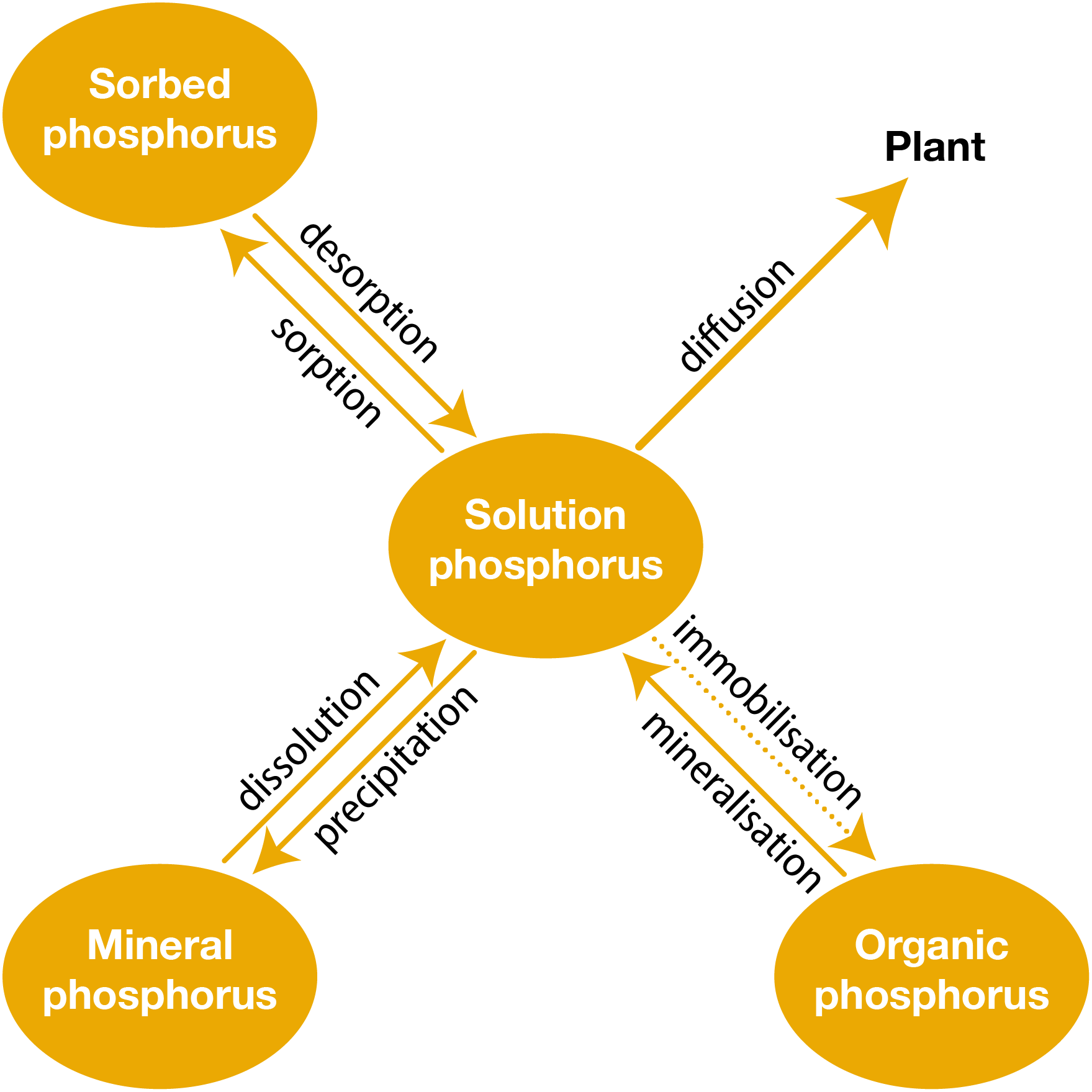
Soil phosphorus pools
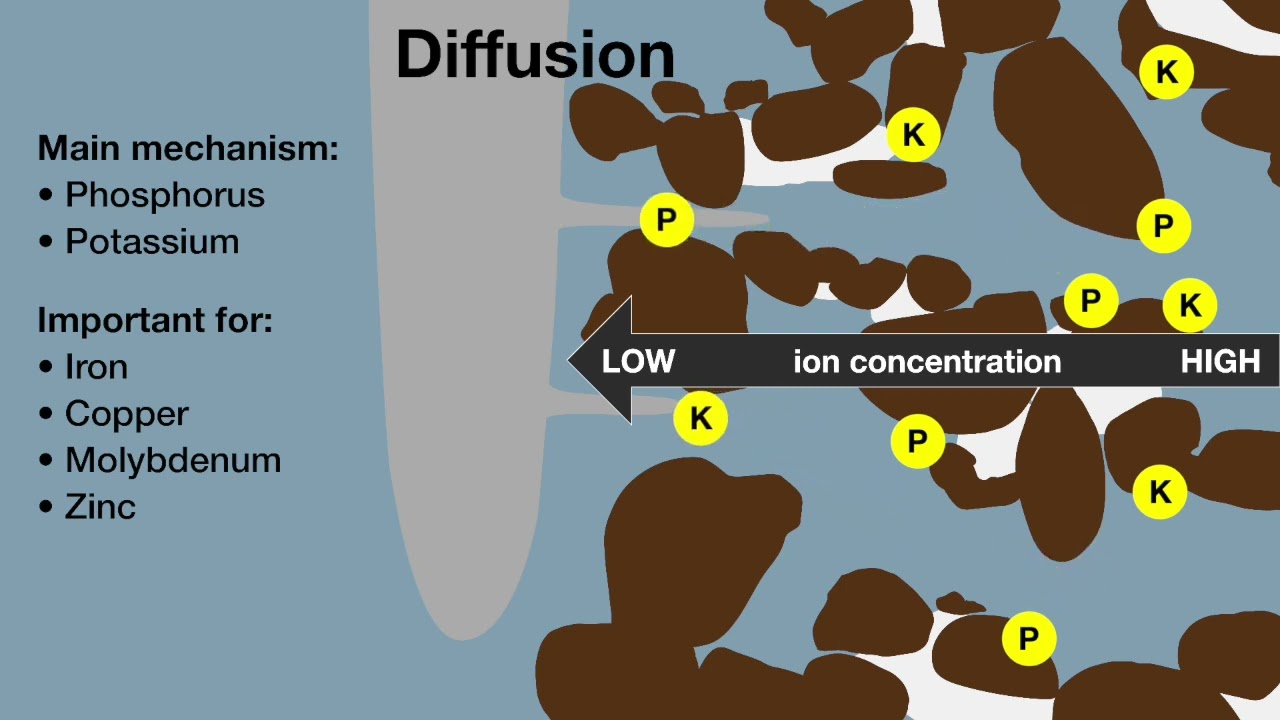
Soil contains phosphorus that can be conceptualised as four pools: solution phosphorus, sorbed phosphorus, mineral phosphorus and organic phosphorus. The phosphorus pools are in equilibrium via the concentration of solution phosphorus. For example, when the concentration of solution phosphorus is lowered by root uptake, some of the sorbed phosphorus will be desorbed until a new sorbed – solution phosphorus equilibrium is reached. When the concentration of solution phosphorus is very low, dissolution of some mineral phosphorus will occur until a new equilibrium is reached with solution phosphorus. The contribution of organic phosphorus to solution phosphorus depends on the relative rates of mineralisation and immobilisation.
The amount of phosphorus measured by a soil test is dependent on the amount of phosphorus present in each pool and the ability of the soil test method to extract phosphorus from each pool. For the test to be a useful predictor of crop yield responses to fertiliser phosphorus, the test must measure phosphorus that is available to crops for the soil-crop system in question.
Colwell P soil phosphorus test
In a Colwell phosphorus test, an extract is obtained by adding a soil sample to a sodium bicarbonate solution adjusted to pH 8.5, and agitating for 16 hours. This extract is then acidified before its phosphorus concentration is measured colorimetrically. The Colwell method measures sorbed and solution phosphorus, but does not provide any information on the equilibrium between these two pools, which is determined by the phosphors buffering capacity of the soil. The phosphorus buffering index (PBI) is used in combination with Colwell-P to assess the levels of soil P supply to crops and pastures. As the phosphorus buffering index increases, the level of Colwell-P required to provide a sufficient level of phosphorus for crops and pastures increases.
DGT-P soil phosphorus test
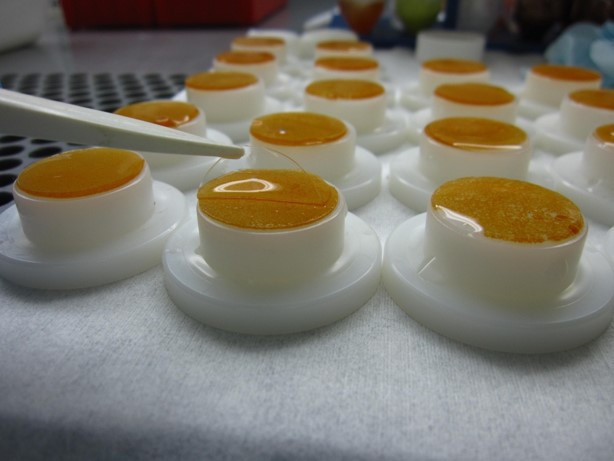
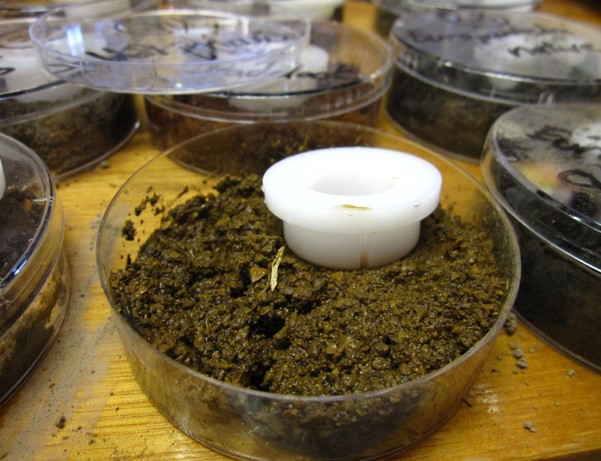
The diffusive gradients in thin films method for phosphorus (DGT-P) was developed for soils where dissolution and precipitation reactions have a dominant role in soil phosphorus supply. In the DGT-P test, a plastic device that includes a diffusive gel and an iron oxide membrane is placed on a moist soil sample. After 24 hours, the amount of phosphorus in the soil that is absorbed into the iron oxide membrane is measured. The phosphorus measured incorporates the initial soil solution phosphorus concentration, and also, the ability of the soil to resupply the soil solution in response to the removal of phosphorus, mimicking the action of plant roots better than other test methods.
References
ebook Soil Quality 10: Plant Nutrition
Scanlan C, Bell R, Weaver D, Borrett R, and Cheng M (2023).
Journal article A simple phosphorus buffering index for Australian Soils
Burkitt L, Moody P, Gourley C, Hannah M (2002). Australian Journal of Soil Research 40, 497-513.
Journal article Prediction of wheat response to an application of phosphorus under field conditions using diffusive gradients in thin-films and extraction methods.
Mason S, McNeill A, McLaughlin MJ and Zhang H (2010). Plant and Soil 337, 243-258.